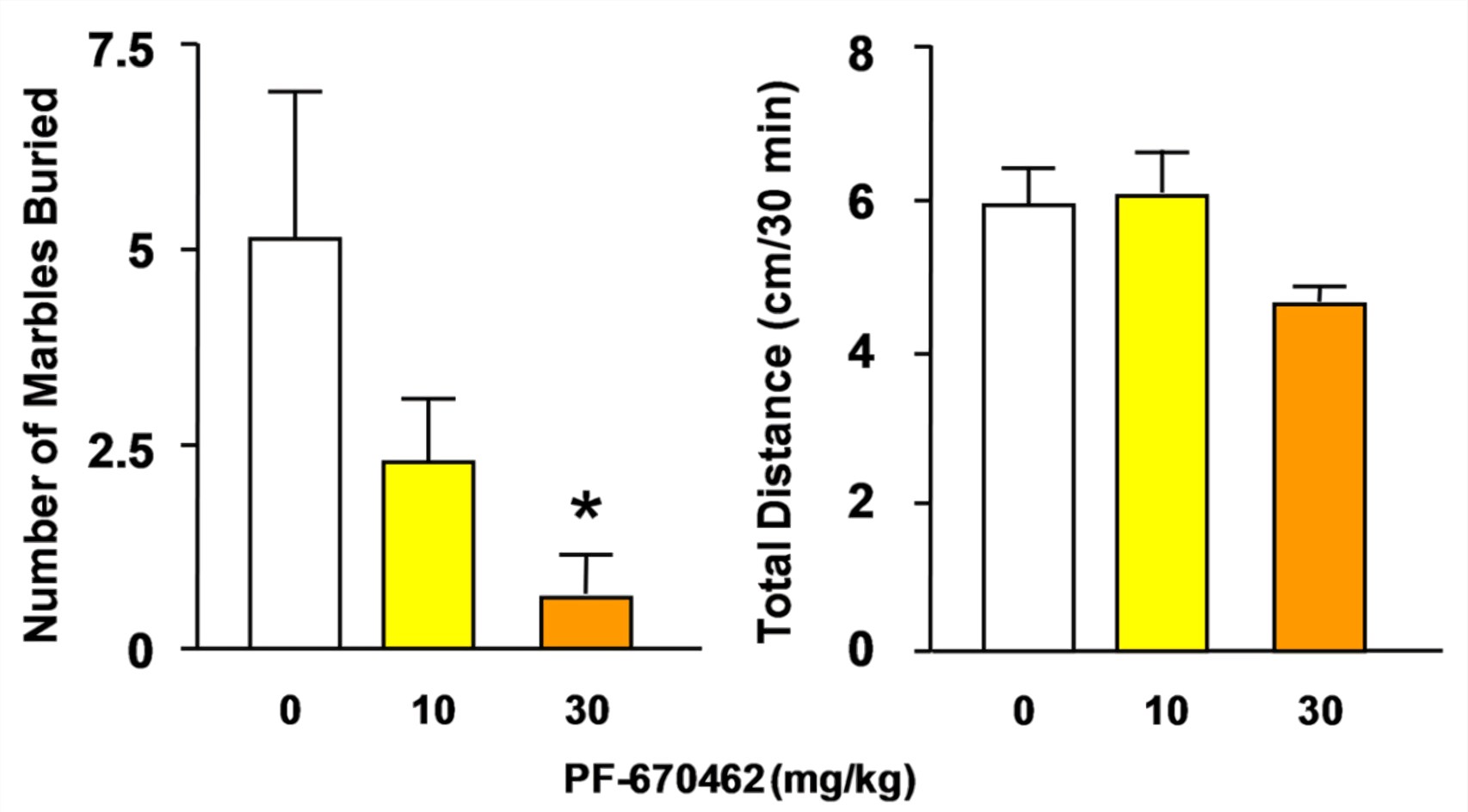
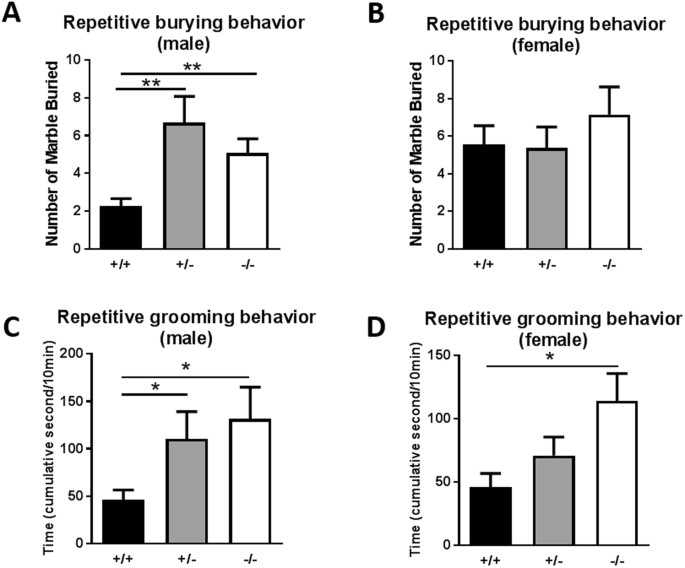
In the current study significant differences in marble burying behavior were observed between pm 2 5 exposed and control rats figure 1b and supplementary figure 3 f 3 35 37 56 p 001.
Marble burying test autism.
The marble burying test protocol described below is modified from deacon 2006 and angoa perez kane.
The marble burying test occurred 8 days following the grooming test to ensure there were no potential residual effects from the initial drug treatment birdsall et al 1978.
The marble burying test takes advantage of the proclivity of mice to dig in natural settings e g.
If a transparent ceiling with breathing holes is placed on top of testing cage this will prevent the test subject from leaving the cage while allowing unrestricted video recording.
The number of marbles that were buried by the mouse was measured.
Each mouse was placed for 45 min into a clean rat cage with 4 cm deep bedding and 12 glass marbles placed on the surface.
Subjects received a different treatment before marble burying from that administered during the spontaneous self grooming experiment with the exception of three b6 mice.
For the communication domain neonatal ultrasonic vocalization and olfactory habituation test toward social and non social odor are described.
In this unit behavioral tests are described that are relevant to the domains affected in asd.
The marble burying test is commonly used to detect repetitive digging behavior servadio et al 2015.
The marble burying test in animal models of asd such as the btbr t tf j mouse eif4e transgenic mice 4e tg as well as in the maternal immune activation mouse model amodeo et al 2012.
Marble burying test and self grooming behavior.
For the repetitive domain the t maze spontaneous alternation test and marble burying test are described.
When put in a cage with marbles mice with ocd like symptoms tend to engage in a high degree of repetitive behaviors including digging while mice with a high degree of anxiety tend to engage in a high degree of digging in novel contexts potentially as a means to attempt.
Santini et al 2013.
Burrows escape tunnels and in standard cage bedding and the nestlet shred test capitalizes on the fact that mice are nesting animals by nature that build nests for protection of themselves and their offspring against environmental conditions e g.
The setup for the marble burying test consists of a standard mouse housing cage filled with a thick layer 5 cm of shaved aspen bedding.
While widely used there is significant controversy over the interpretation of its results.
It is based on the observation that rats and mice will bury either harmful or harmless objects in their bedding.